Maintenance leaders are under constant pressure to reduce downtime, control costs, and improve asset reliability without increasing headcount. At the same time, technology vendors are pushing artificial intelligence as the next big leap in maintenance management. This has created a serious strategic question for plant heads, facility managers, and reliability engineers: should you invest in AI-driven maintenance, or continue with structured rule-based scheduling?
The answer is not as simple as choosing “old vs new.” Both approaches serve different operational realities. Some assets respond well to time-based or meter-based preventive maintenance. Others show unpredictable failure patterns that only data models can detect early.
This article breaks down AI maintenance vs rule-based scheduling in technical depth, helping you evaluate cost, risk, data maturity, and organizational readiness before choosing the right path to reliability.
What is rule-based scheduling in maintenance management?
Rule-based scheduling is the traditional backbone of preventive maintenance. It relies on predefined logic such as time intervals, usage counters, or threshold conditions to automatically trigger work orders inside a CMMS.
These rules are created by reliability engineers based on OEM manuals, historical failure data, and operational experience. Once configured, the system generates maintenance tasks at fixed intervals or when predefined limits are reached.
Key characteristics of rule-based maintenance scheduling:
- Time-based triggers such as every 30 days, 90 days, or annually.
- Meter-based triggers such as every 1,000 operating hours or 10,000 cycles.
- Threshold-based alerts, such as temperature exceeding a safe limit.
- Deterministic execution, meaning the same condition always produces the same work order.
- Clear compliance documentation is useful for audits and regulated industries.
Rule-based scheduling is highly structured, predictable, and easy to audit. However, it does not adapt dynamically to changing asset behavior.
What is AI-driven maintenance and predictive maintenance?
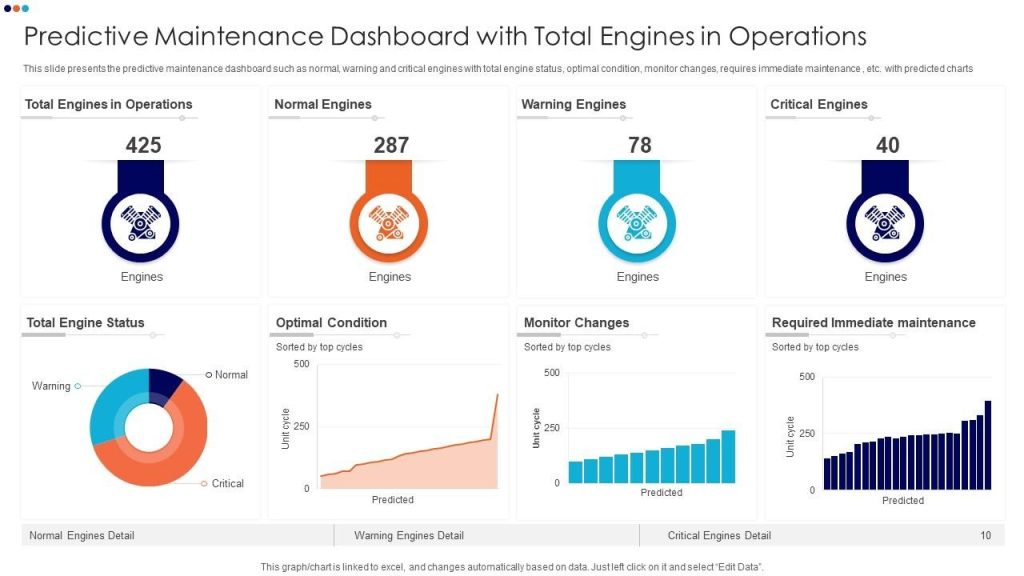

AI maintenance, often implemented as predictive maintenance, uses machine learning algorithms to analyze asset data and estimate failure probability or remaining useful life.
Instead of relying on fixed intervals, ai models examine patterns in vibration, temperature, pressure, current draw, runtime logs, and historical breakdown events. The system detects anomalies or degradation trends that indicate potential failure before it happens.
Core elements of AI-driven maintenance:
- Continuous data collection from sensors and operational systems.
- Machine learning models trained on historical failure patterns.
- Risk scoring or failure probability outputs.
- Dynamic work order generation based on predicted risk.
- Feedback loops for model retraining and improvement.
Unlike rule-based systems, AI maintenance adapts to changing operating conditions and asset health trends.
Strengths of rule-based scheduling
Rule-based maintenance remains widely used across manufacturing, facility management, utilities, and infrastructure for good reason. It offers stability and operational clarity.
- Predictable workload planning
Maintenance managers can forecast labor hours, spare part consumption, and contractor requirements with high consistency. - Lower implementation complexity
There is no need for advanced data science skills, complex model validation, or data engineering pipelines. - Strong audit and compliance support
Industries such as pharmaceuticals, aviation, and food processing often require documented preventive maintenance cycles. Rule-based systems are straightforward to justify during inspections. - Suitable for low-criticality assets
For assets with simple wear-out patterns, fixed-interval maintenance is often sufficient. - Lower initial investment
Organizations without advanced sensor infrastructure can still implement effective preventive maintenance.
However, rule-based systems may lead to over-maintenance if intervals are conservative.
Strengths of AI-driven maintenance
AI maintenance is particularly powerful in complex industrial environments where downtime is expensive and failure modes are variable.
- Reduction in unplanned downtime
AI systems detect early warning signs before functional failure occurs. - Maintenance only when needed
Instead of replacing parts on schedule, assets are serviced based on actual condition. - Improved spare parts optimization
Inventory can be aligned with predicted failure windows. - Better insight into complex failure patterns
AI models can detect nonlinear degradation patterns that static rules cannot capture. - Continuous learning
Models improve over time as more data becomes available.
For high-value rotating equipment, critical compressors, turbines, or automated production lines, predictive maintenance can significantly improve reliability metrics such as MTBF and availability.
Limitations and risks to consider
Both approaches carry operational and financial risks if poorly implemented.
Limitations of rule-based scheduling:
- Risk of unnecessary maintenance activities.
- Inability to detect early anomalies outside predefined thresholds.
- Rule complexity increases as asset diversity grows.
- Limited adaptability to changing operational loads.
Limitations of AI-driven maintenance:
- Requires high-quality, continuous data streams.
- Significant upfront investment in sensors and infrastructure.
- Model drift if operating conditions change.
- Need for explainability to gain technician trust.
- Requires data science and analytics capability.
Organizations must evaluate internal capability before adopting AI-based maintenance solutions.
How to choose between AI maintenance and rule-based scheduling
Choosing the right maintenance strategy depends on multiple operational factors.
1. Asset criticality
If equipment failure leads to safety risk, regulatory impact, or high production loss, AI-based predictive maintenance may justify the investment.
Low-risk assets with minimal operational impact may remain on rule-based schedules.
2. Data maturity
Do you have reliable sensor data, structured failure logs, and consistent asset history? Without quality data, AI maintenance will underperform. If data is limited, start with rule-based scheduling while building digital infrastructure.
3. Failure behavior
Assets with consistent wear-out patterns are suitable for fixed intervals. Assets with variable or unpredictable failure modes benefit from predictive models.
4. Organizational readiness
Do you have internal analytics expertise or a reliable technology partner? AI maintenance requires governance, validation, and ongoing model management.
5. Budget and roi expectations
AI systems require capital expenditure and operational expenditure. Calculate expected reduction in downtime, spare parts savings, and productivity gains before committing.
The hybrid approach: combining AI and Rule-based maintenance
In many industrial environments, the best strategy is not choosing one over the other but combining both.
A hybrid maintenance strategy may include:
- Rule-based preventive maintenance for low-risk or compliance-driven assets.
- AI-driven predictive monitoring for high-value critical equipment.
- Condition-based triggers are validated by technicians before work order approval.
- Governance frameworks define when AI overrides scheduled maintenance.
This layered approach allows gradual digital transformation without operational disruption.
Implementation roadmap for maintenance leaders
If you are evaluating AI maintenance vs rule-based scheduling, consider this phased roadmap:
- Classify assets by criticality and failure impact.
- Establish baseline reliability metrics such as MTBF, MTTR, and downtime cost.
- Strengthen CMMS data quality and work order discipline.
- Pilot predictive maintenance on a small set of critical assets.
- Compare predictive alerts against existing rule-based schedules.
- Scale gradually based on measurable reliability improvement.
This structured transition minimizes risk while improving long-term asset reliability.
Summing it up
AI maintenance vs rule-based scheduling is not a debate about old versus new technology. It is a strategic reliability decision based on asset behavior, data readiness, cost structure, and organizational maturity.
Rule-based scheduling offers stability, compliance, and low complexity. AI-driven maintenance delivers dynamic insight and targeted interventions for high-risk assets. The right path to reliability often lies in a thoughtful combination of both.
For maintenance leaders, the goal is not to chase technology trends but to build a sustainable maintenance strategy that reduces downtime, optimizes cost, and improves asset performance year after year.