In any production-driven environment, machine efficiency isn’t just a target—it’s a foundation for profits, product quality, and timely delivery. One of the most advanced metrics for tracking equipment effectiveness is Total Effective Equipment Performance, often shortened as TEEP. This metric expands on the well-known OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness) by offering a more comprehensive view of how effectively equipment is used in relation to its full potential.
Unlike OEE, which only considers scheduled production time, TEEP pushes the boundary further by evaluating performance against all 24 hours of available time, 7 days a week. This makes it a critical metric for identifying hidden capacity, optimizing asset utilization, and making informed capital investment decisions.
Understanding the concept of TEEP
TEEP is a measure that combines OEE with equipment utilization. While OEE tracks how well equipment performs during planned production time, TEEP gives you insight into how much of the total available calendar time is being converted into actual productive output. It’s a blend of both operational efficiency and planning efficiency.
For industries with fixed capital assets, limited floor space, or fluctuating customer demand, TEEP provides a roadmap to improve machine availability without necessarily investing in new equipment. It highlights whether improvements are needed in production scheduling, equipment reliability, or even workforce planning.
How is TEEP calculated?
The TEEP formula integrates both OEE and utilization, offering a full-scale view of equipment productivity across total available time. Here’s the breakdown:
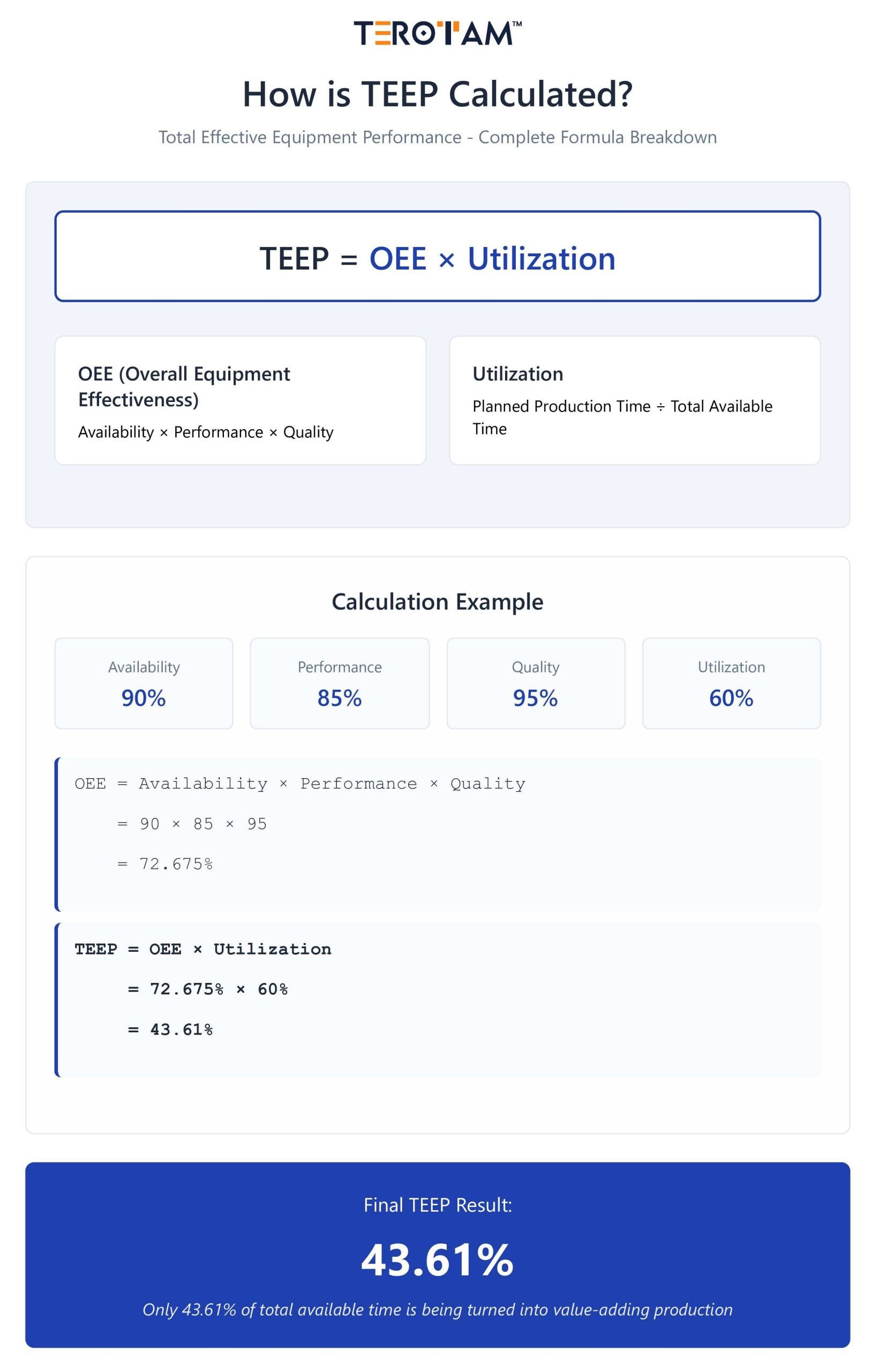
TEEP = OEE × Utilization
- OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness) = Availability × Performance × Quality
- Utilization = Planned Production Time / Total Available Time
For example, if your equipment has:
- Availability: 90%
- Performance: 85%
- Quality: 95%
- Utilization: 60%
Then:
- OEE = 0.90 × 0.85 × 0.95 = 72.675%
- TEEP = 72.675% × 60% = 43.61%
This tells you that only 43.61% of the total available time is being turned into value-adding production.
Key components that influence TEEP
Before you can improve TEEP, it’s important to understand the levers that impact it. Each component provides different types of insight and calls for different strategies to improve.
- Availability losses
These are caused by equipment breakdowns, setup delays, or changeovers. High downtime eats into both OEE and TEEP, reducing actual run time. - Performance losses
These occur when machines run slower than their rated speed. Speed losses might stem from worn-out parts, suboptimal process settings, or inconsistent material flow. - Quality losses
Rejected parts, rework, and scrap directly lower your yield. Consistent process monitoring and real-time quality checks help maintain high-quality output. - Utilization gaps
Even with a good OEE score, low utilization can mean that the equipment sits idle for long hours. This could be due to poor production planning, low order volumes, or labor availability.
Why should industries track TEEP?
Monitoring TEEP gives manufacturers a broader view of where their equipment capacity is going unused and what actions can unlock more output. Here’s how TEEP becomes valuable:
- Capacity planning and capital investment
TEEP helps determine if existing equipment can handle increased demand or if investing in new machines is necessary. - Hidden time recovery
Idle hours due to non-production days or shifts are often overlooked. TEEP brings attention to this hidden time. - Strategic scheduling
By improving utilization through better shift planning or longer production runs, businesses can boost productivity without increasing overhead. - Continuous improvement
TEEP can be used alongside lean practices to track gains from process improvements, TPM (Total Productive Maintenance), or Six Sigma initiatives.
Tips to improve your TEEP score
Improving TEEP isn’t about pushing equipment harder—it’s about working smarter. Here are a few strategies that help:
- Balance workloads across available time
Introduce extra shifts, weekend runs, or staggered schedules to raise utilization. - Reduce setup and changeover time
Quick changeover techniques and better scheduling reduce idle periods and downtime. - Implement real-time monitoring
Use IoT tools or CMMS software to monitor performance and detect issues before they lead to stoppages. - Train operators for multi-skilling
Multi-skilled workers ensure equipment isn’t sitting idle due to labor shortages or specialist dependency. - Align production with demand
Avoid overproduction or underutilization by syncing manufacturing cycles with real-time demand forecasts.
Final thoughts
TEEP takes the concept of equipment efficiency to the next level by measuring how much of your available time is truly turned into productive output. While OEE remains a strong performance metric during active production, TEEP shines a light on untapped capacity and scheduling inefficiencies. For businesses aiming to increase throughput without additional investment, tracking and improving TEEP can be a game-changing move.Want help improving your TEEP with digital tools and smart asset monitoring? – Write to us at contact@terotam.com and let our experts show you how.