Manufacturing is the backbone of every country’s economy and GDP and the lifeblood of any product or goods manufacturing unit, so every pause carries weight.
Now you must be thinking, what kind of pause are we talking about? We are talking about anticipated or unanticipated pauses that occur because of downtime.
Downtime casts its silent influence over the factory floor. Like a fleeting guest overstaying its welcome, it disrupts the rhythm of operations, leaving its mark on efficiency and productivity.
In this article, we take a close look at meaning and types of downtime in manufacturing, exploring its causes and effects with a touch of idea about how CMMS software can be a solution.
Downtime in Manufacturing
Understanding downtime in manufacturing necessitates carefully examining its operational dynamics and consequences. Downtime, or the short-term interruption of productive activity within a manufacturing facility, covers various events, from scheduled maintenance to unforeseen equipment breakdowns. Within this spectrum, downtime has two forms: planned and unplanned.
From a technical standpoint, downtime can be measured and analyzed using key performance indicators (KPIs) such as Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) and Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF).
OEE provides insights into equipment performance, availability, and quality, enabling manufacturers to identify areas for improvement and optimize production processes. MTBF quantifies equipment reliability by calculating the average time elapsed between failures, allowing maintenance teams to implement preventive measures and minimize unplanned downtime.
Understanding these technical aspects of downtime empowers manufacturing organizations to proactively manage their assets, enhance operational efficiency, and mitigate the impact of disruptions on production schedules.
Planned vs. Unplanned Downtime
Planned and unplanned downtime represent two distinct categories within the realm of manufacturing interruptions, each with its own characteristics, implications, and management strategies.
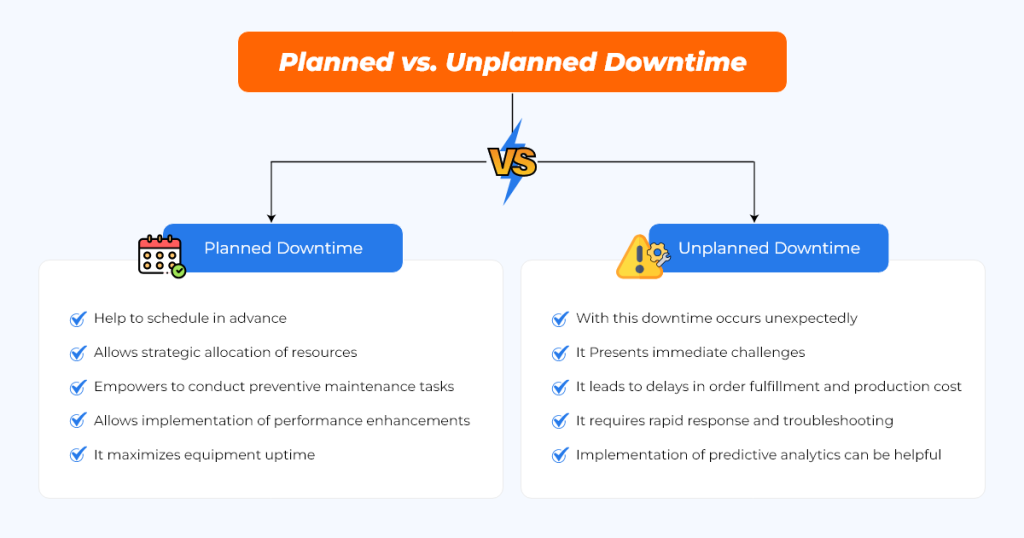
Planned Downtime:
- Planned downtime is scheduled in advance for maintenance, upgrades, or adjustments.
- It allows for strategic allocation of resources and minimizes disruptions to workflow.
- It offers the opportunity to conduct preventive maintenance tasks and address known issues.
- It enables the implementation of performance enhancements to equipment and processes.
- It maximizes equipment uptime, extends asset lifespan, and optimizes operational efficiency.
- It can be managed and minimized through preventive measures and strategic planning.
Unplanned Downtime:
- Unplanned downtime occurs unexpectedly due to equipment failures, malfunctions, or unforeseen events.
- It Presents immediate challenges to manufacturing operations and productivity.
- It also leads to delays in order fulfillment, increased production costs, and potential damage to reputation.
- It requires rapid response and troubleshooting to identify root causes and implement corrective actions.
- Unplanned downtime can be mitigated through proactive maintenance practices and real-time equipment health monitoring.
- Implementation of predictive analytics helps anticipate and prevent potential failures before they occur.
How to Measure Downtime in a Manufacturing Facility?
Measuring downtime in a manufacturing facility involves employing various methods and metrics to accurately quantify production process interruptions and their impact.
Here are key concepts and strategies for effective downtime measurement:
- Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE): Evaluate equipment performance, availability, and quality to identify areas for improvement.
- Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF): Calculate the average time between equipment failures to predict downtime frequency and improve reliability.
- Mean Time to Failure (MTTF): Estimate the average time until equipment failure for non-repairable components.
- Mean Time to Repair (MTTR): Measure the average time required to repair equipment and minimize downtime duration.
- Downtime Tracking Software: Utilize CMMS software for real-time tracking, categorization, and analysis of downtime events.
- Downtime Logs and Reports: Maintain detailed logs and reports of downtime incidents to track trends and prioritize improvement efforts.
- Root Cause Analysis (RCA): Identify underlying causes of downtime to implement corrective actions and prevent recurrence.
- Utilization of Sensors and IoT Devices: Implement sensors and IoT devices for real-time monitoring of equipment health and performance metrics.
CMMS Software: The Ultimate solution to reduce downtime and Its Effects
Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS) offer a proactive approach to managing downtime and its effects in manufacturing environments.
By leveraging CMMS solutions, manufacturers can achieve the following:
Scheduled Maintenance:
Implementing preventive maintenance schedules to minimize the risk of unplanned downtime and extend equipment lifespan.
Real-Time Monitoring:
Utilizing sensors and preventive maintenance analytics to monitor equipment health and detect potential failures before they occur.
Inventory Management:
It is ensuring timely availability of spare parts and materials to expedite repairs and minimize downtime.
Work Order Management:
Streamline maintenance workflows and allocate resources efficiently to address maintenance needs promptly.
Data-driven Decision Making:
Analyzing downtime data and performance metrics to identify root causes and implement targeted improvements.
Training and Skill Development: Investing in training programs to empower maintenance teams with the skills and knowledge necessary to troubleshoot and resolve issues effectively.
Conclusion
Downtime remains a formidable challenge for manufacturers worldwide, impacting productivity, profitability, and competitiveness. However, with the right strategies and technologies in place, such as CMMS solutions, manufacturers can mitigate the effects of downtime and unlock new levels of efficiency and reliability in their operations.Want to know more from experts? – connect with us now or write us at contact@terotam.com